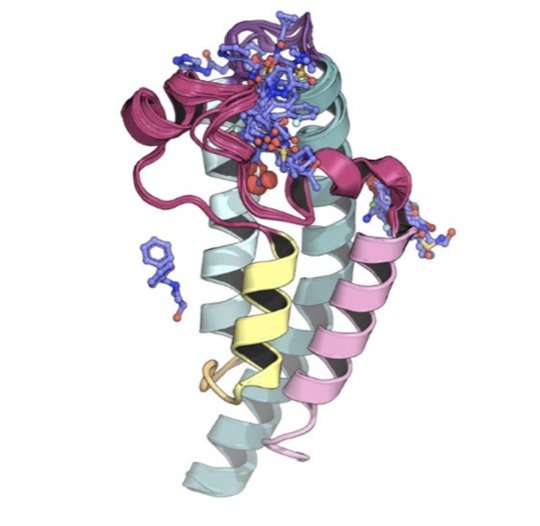
SAMPL7 protein-ligand challenge: A community-wide evaluation of computational methods against fragment screening and pose-prediction
/Grosjean H, Isik M, Aimon A, Mobley D, Chodera JD, von Delft F, and Biggin PC
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design 36:291, 2022 [DOI]
We field a blind community challenge to assess how well state of the art computational chemistry methods can predict the binding modes of small druglike fragments to a protein target for which no chemical matter is known, PHIP2, using fragment screening at the Diamond Light Source.