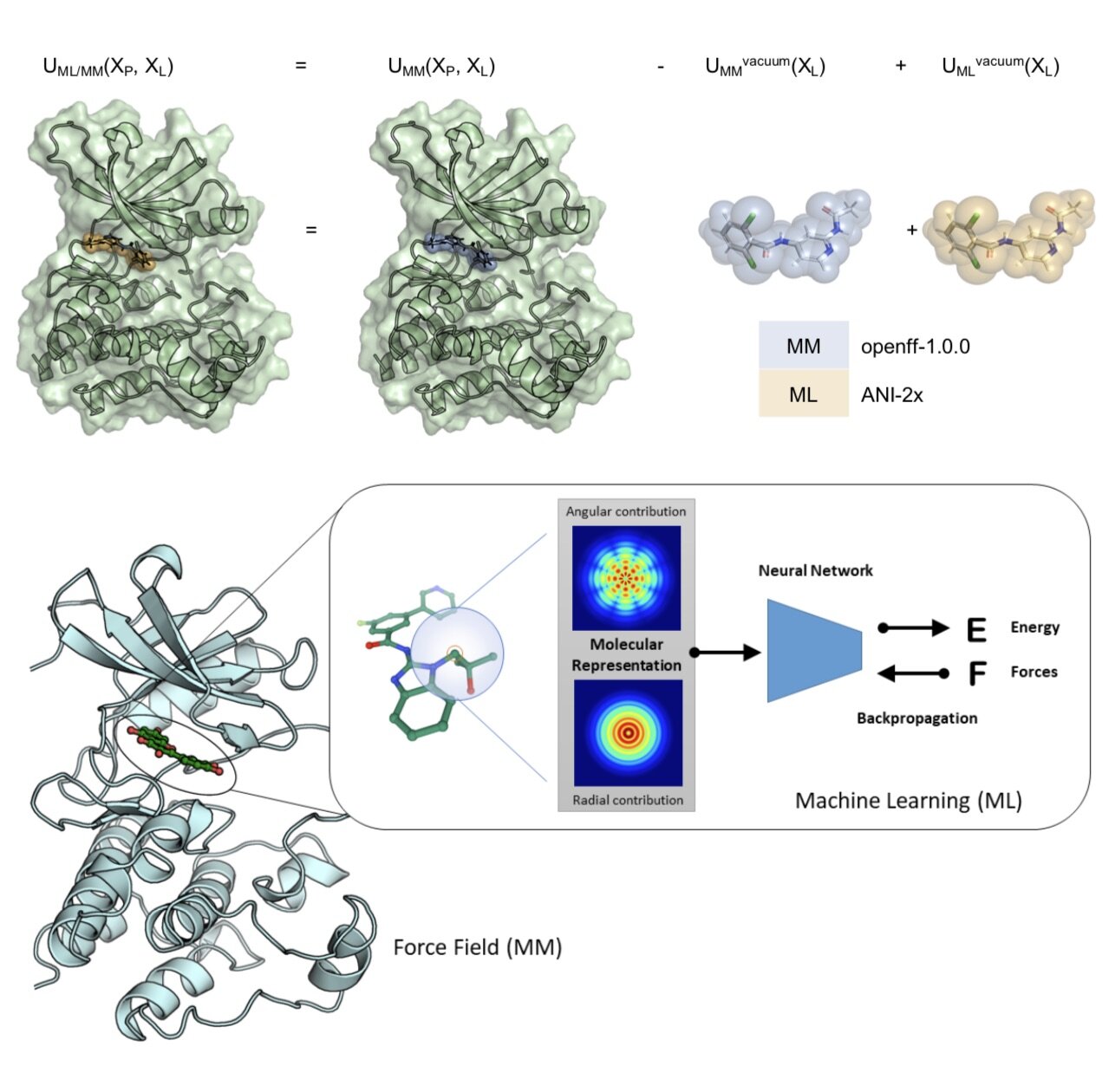
Identifying and Overcoming the Sampling Challenges in Relative Binding Free Energy Calculations of a Model Protein:Protein Complex
/Zhang I, Rufa DA, Pulido I, Henry MM, Rosen LE, Hauser K, Singh S, Chodera JD
Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation 19:4863, 2023
We assess what is required for alchemical free energy calculations to be able to make high-quality predictions of the impact of interfacial mutations on protein-protein binding.